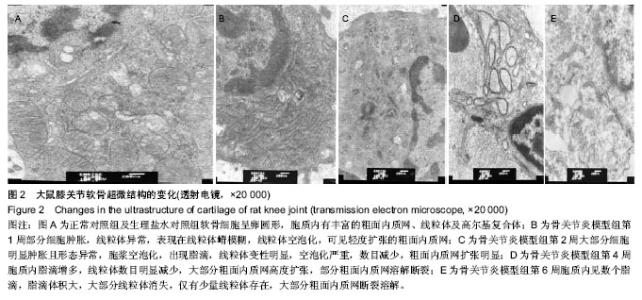
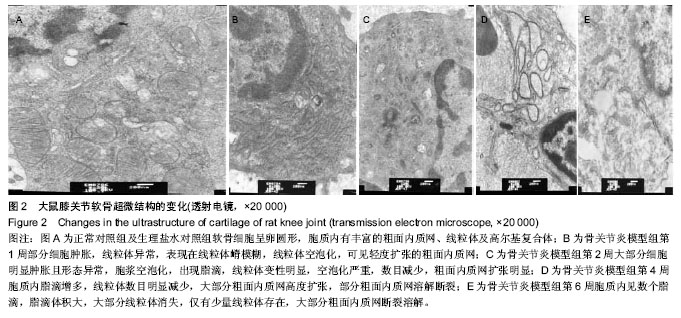
| [1] Li X, Lang W, Ye H, et al.Tougu Xiaotong capsule inhibits the tidemark replication and cartilage degradation of papain- induced osteoarthritis by the regulation of chondrocyte autophagy. Int J Mol Med. 2013; 31(6):1349-1356.
[2] 梁彦勤,廖荣臻,刘超,等.骨性关节炎动物模型研究概况[J].广西中医药大学学报,2012,15(3):64-66.
[3] 邓宇,筱梅,任医民,等.关节腔内注射不同蛋白酶建立兔膝骨关节炎模型的对比研究[J].中华关节外科杂志,2009,3(3):332-338.
[4] 王庆蓉,官颖鹏,邵卫.软骨细胞在膝骨性关节炎中的超微结构改变[J].电子显微学报,2000,19(6):819-823.
[5] 曾庆徐,黄少弼,肖征宇.症状性骨关节炎临床和流行病学探讨[J].中华内科杂志,1995,34(2):88-90.
[6] Bendele AM. Animal models of osteoarthritis in an era of molecular biology. JMusculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2002; 2(6):501-503.
[7] Young MF. Mouse models of osteoarhritis provide new research tools. Trends Phamacol Sci.2005;26(7):333-335.
[8] 杨峰,史宗道.用木瓜蛋白酶建立兔颞颌关节骨关节炎模型的研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2002,20(10):330.
[9] Okazaki R,Sakai A,Ootsuyama A,et al.Apoptosis and p53Expresson in Chondrocytes Relate to Degeneration in Articular Cartilage of Immobilized Knee Joints. Rheumatol. 2003;30(3):559-566.
[10] Wancket LM,Baragi V,Bove S.Anatomical localization of cartilage degradationmarkers in a surgically induced ratosteoarthritismodel.Toxicologic pathology.2005;33(4):484.
[11] Mosikowitiz RW. Experimental models of osteoarthritis. Innosteoarthristis Saunders.Philadelphia.1984;109-115.
[12] Bunger C,Hjermind J,Harving S,et al.Relationship between introasseous pressures and intra-articular pressures in arthritis of the knee.Acta Orthop Scand.1983;54(2):188-193.
[13] Lozoya KA,Flores JB.A novel rat osteoarthrosis model to assess apoptosis and matrix degradationpathol.Res Pract. 2000;196(11):729-745.
[14] 吴宏斌,杜靖远,胡勇,等.兔前交叉韧带切断骨关节炎模型中MMP-1、MMP-13及TIMP-1的mRNA表达研究[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2002,6(3):169.
[15] 王健,敖英芳.后交叉韧带断裂继发关节软骨退行性变的实验研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2004,23(5):476.
[16] 顾廷,戴克戎,裘世静,等.应力降低导致关节软骨退变机理的形态学研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1995,15(9):631-633.
[17] 毛宾荛.膝关节痛与膝关节骨内压[J].中华骨科杂志,1993, 13(20): 137-139.
[18] 陈宝兴,丁继华.双后肢大白鼠的骨关节病实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1986,7(2):96.
[19] 沈培芝,石印玉.强筋方治疗试验性膝骨关节炎的组织病理学观察研究[J].中国中医骨伤科,1995,3(1):10-13.
[20] 路磊,王竞.关节不稳定诱发家兔膝关节骨关节炎的实验研究[J].局解手术学杂志,1995,4(1):23-24.
[21] 陈宏贤,王大平,牛琼,等.骨关节炎动物模型的建立及选择[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2008,18(4):209-212.
[22] Aigner T,Cook JL,Gerin N.et al.Histopathology atlas of animal model systems-overview of guiding principles.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2010;18(3):2-6.
[23] Kikuchi T,Sakuta T,Yamaguchi T.Intra-articular injection of collagenase induces experimental osteoarthritis in mature rabbits.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.1998;6(3):177-186.
[24] Tsai CL,Liu TK.Estradiol-induced knee osteoarthrosis in ovariectomized rabbits.Clin Orthop.1993;(291):295-302.
[25] 邓宇,伍筱梅,任医民,等.关节腔内注射不同蛋白酶建立兔膝骨关节炎模型的对比研究[J].中华关节外科杂志2009,3(3):332-339.
[26] Han GY, Ling PX, Wang FS, et al.Comparison study on knee osteoarthritis in rabbits induced by different concentrations of papain,Zhongguo Gu Shang.2012:25(5):424-429.
[27] 孙鲁宁,赵燕华,黄桂成.木瓜蛋白酶诱导膝关节骨关节炎模型兔滑膜病理变化与药物注射时间的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(50):9311-9316.
[28] 华英汇,顾湘杰,陈世益,等.威灵仙注射液对骨关节炎影响的实验研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2003,22(4):420-422.
[29] 汪宗保,廖威明,陈朝晖,等.木瓜蛋白酶诱导大鼠膝早期骨关节炎软骨表面的扫描电镜观察[J].中国组织工程研究杂志,2014, 18(2):177-182.
[30] Havdrup T,Telhag H.Papain-induced changes in the knee joints of adult rabbits. Acta Orthop Scand.1977,48(2): 143-149.
[31] 孙鲁宁,黄桂成,赵燕华,等.木瓜蛋白酶诱导兔膝关节骨关节炎模型滑膜中白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、白三烯浓度变化与药物注射时间的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(33):6184- 6188.
[32] 谭庆远,王黎明,曲洪雪,等.中药萃取超导透入治疗兔膝骨关节炎疗效的实验研究[J].中医临床研究,2011,3(3):11-13.
[33] 庄超,刘瑞平,徐南伟,等.兔骨关节炎模型血清炎症指标的动态观察[J].南京医科大学学报,2011,31(3):369-373.
[34] Vignon E, Arlot M, Vignon G. Etude de al densite cellulaire due cartilage delatete femoral en function delage.Rev Rhum Mal Oeteoarthritic.1976;13(4):365.
[35] 娄思权.骨关节炎的病理与发病因素[J].中华骨科杂志,1996, 16(1):56-59.
[36] 石辉,何斌,史晨辉,等.用尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物建立兔骨关节炎模型的研究[J].石河子大学学报,2009,24(1): 66-69.
[37] Muehleman C,Green J,Williams JM,et al.The efect of bone remodels inhibition by the oledronnic acid in an animal model of cartilage matrix damage.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2002; 10(3):226-233.
[38] Kikuchi T ,Sakuta T,Yamaguchi T.Intra-articular injection of collagenase induces experimental osteoarthritis in mature rabbits.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.1998;6(3):177-186.
[39] 杨峰,史素道.用木瓜蛋白酶建立兔颞颌关节骨关节炎模型[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2002,12(5):330-333.
[40] Kopp S, Mejersjo C, Clemenssson E. Induction of osteoarthrosis in the guinea pig knee by papain. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1983;55(3):259-266.
[41] 江捍平,王大平.骨关节炎动物模型[J].中国现代医学杂志2004, 14(6):153-156.
[42] 陈百成,张静.骨关节炎[M].北京: 人民卫生出版社,2006: 199-202.
[43] 张文贤,张晓刚.骨性关节炎的实验研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2003,11(6):51-53.
[44] 柴本甫,汤雪明.实验性骨关节炎超微结构研究[J].上海第二医科大学学报,1988,8(3):193-198.
[45] 唐旭升,杜宁.手法治疗大鼠膝骨关节炎的超微结构研究[J].中医骨伤科杂志,2001,9(2):7-10.
[46] 戴七一,文宗振.逍遥散对雌性兔膝关节软骨细胞超微结构的影响[J].中医正骨,2012,24(9):8-10.
[47] 刘献祥,李西海,周江涛.改良 Hulth造模法复制膝骨性关节炎的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2005,25(12):1104-1108.
[48] 张红宇,赵卫东,高岩峰.O3对骨性关节炎关节软骨作用的MR与电镜观察[J].当代医学,2009,15(35):759-761. |